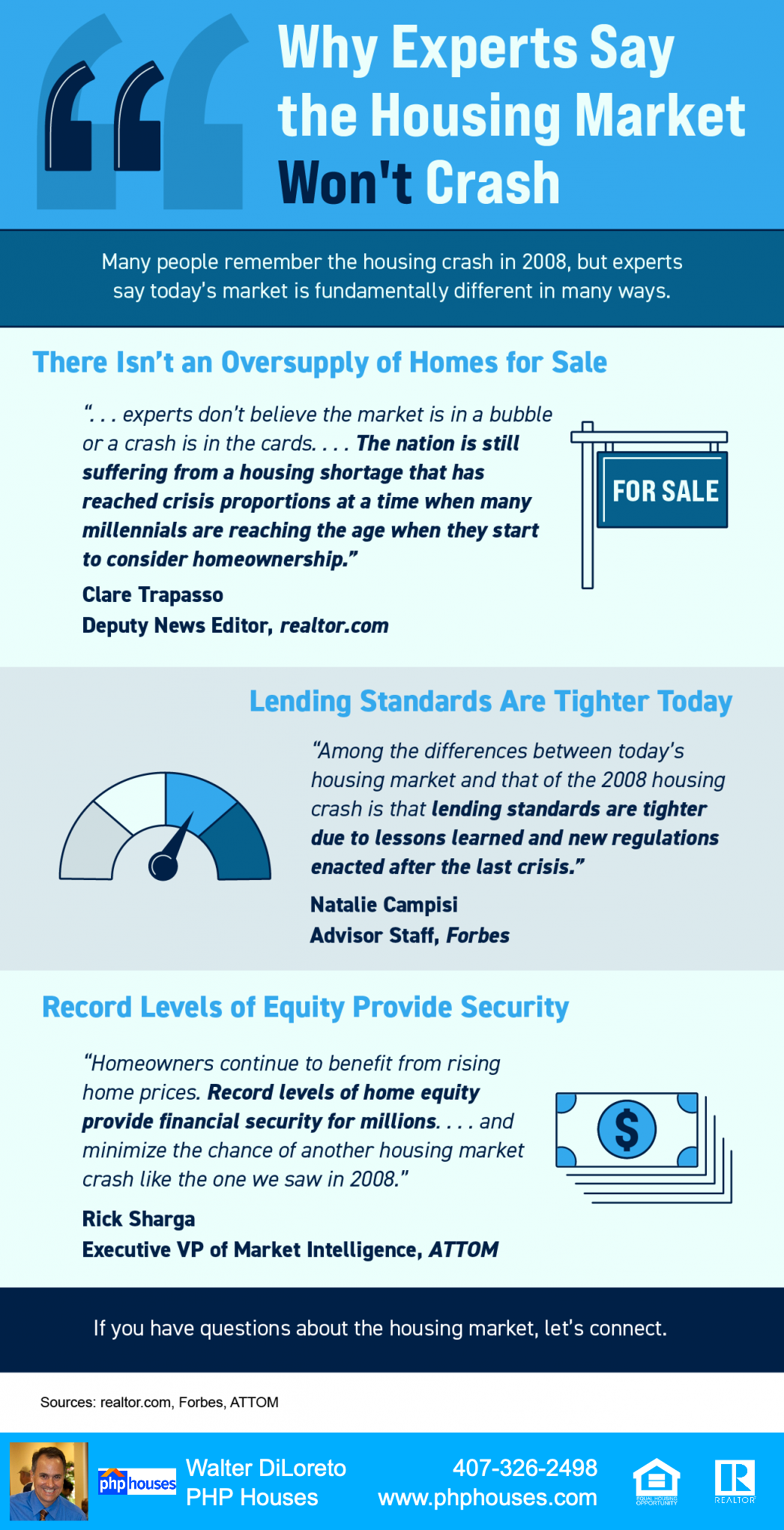
Why Home Loans Today Aren’t What They Were in the Past
In today’s housing market, many are beginning to wonder if we’re returning to the riskier lending habits and borrowing options that led to the housing crash 15 years ago. Let’s ease those concerns.
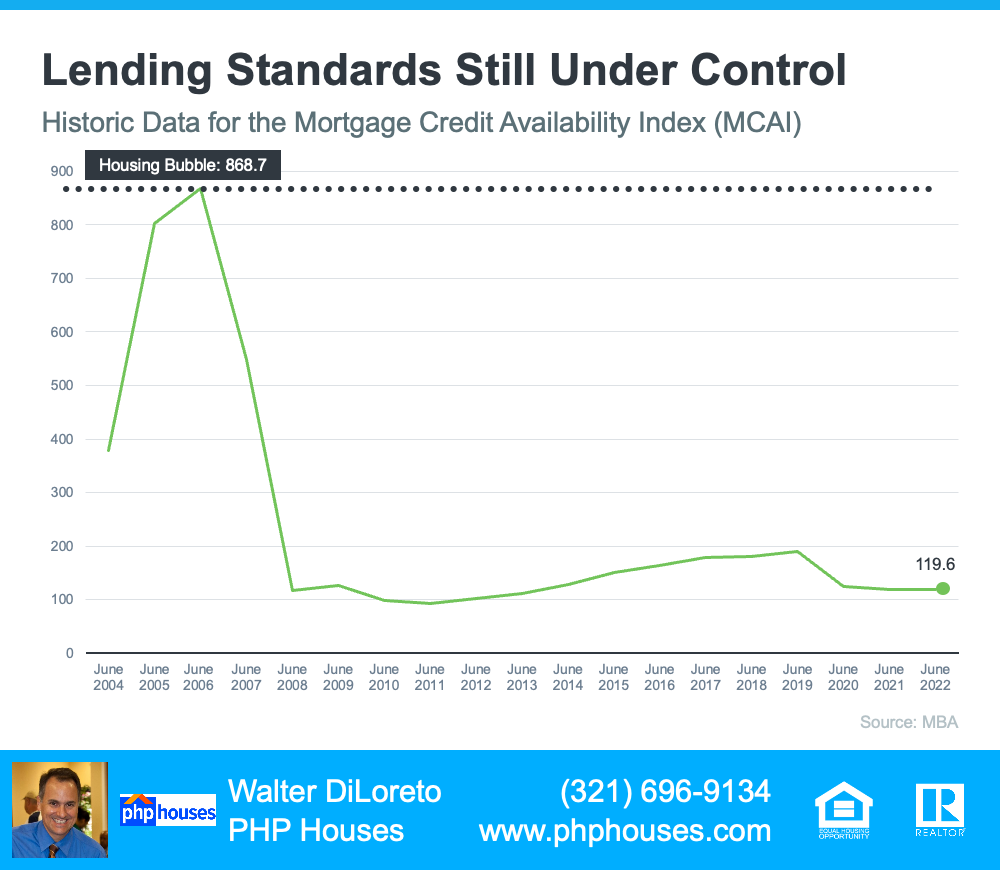
Several times a year, the Mortgage Bankers Association (MBA) releases an index titled the Mortgage Credit Availability Index (MCAI). According to their website:
“The MCAI provides the only standardized quantitative index that is solely focused on mortgage credit. The MCAI is . . . a summary measure which indicates the availability of mortgage credit at a point in time.”
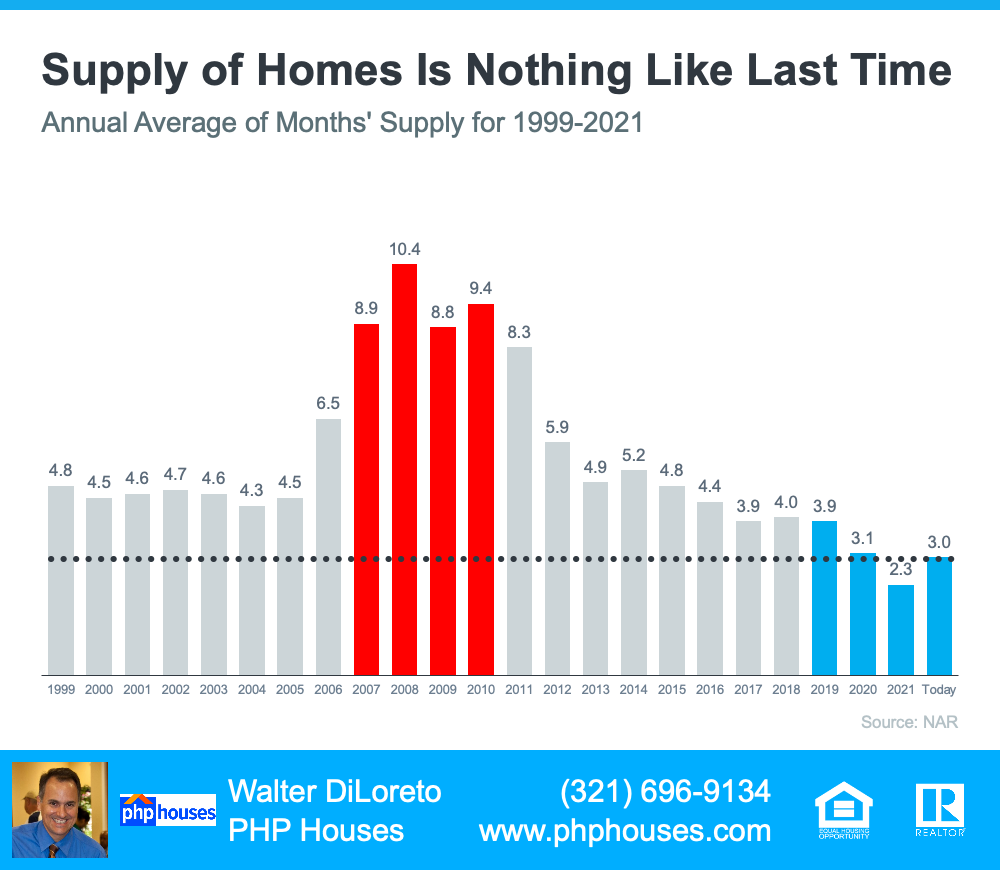
Basically, the index determines how easy it is to get a mortgage. The higher the index, the more available mortgage credit becomes. Here’s a graph of the MCAI dating back to 2004, when the data first became available:
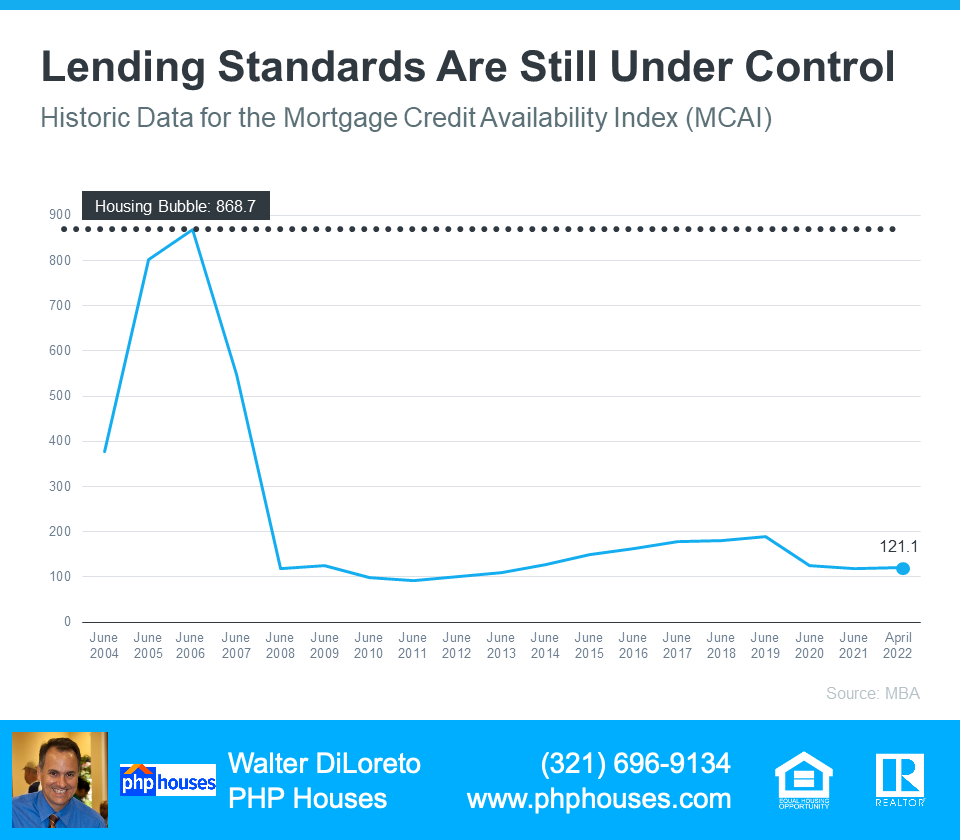
Lending Standards Are Still Under Control
As the graph shows, the index stood at about 400 in 2004. Mortgage credit became more available as the housing market heated up, and then the index passed 850 in 2006. When the real estate market crashed, so did the MCAI as mortgage money became almost impossible to secure. Thankfully, lending standards have eased somewhat since then, but the index is still low. In April, the index was at 121, which is about one-seventh of what it was in 2006.
Why Did the Index Get out of Control During the Housing Bubble?
The main reason was the availability of loans with extremely weak lending standards. To keep up with demand in 2006, many mortgage lenders offered loans that put little emphasis on the eligibility of the borrower. Lenders were approving loans without always going through a verification process to confirm if the borrower would likely be able to repay the loan.
An example of the relaxed lending standards leading up to the housing crash is the FICO® credit score associated with a loan. What’s a FICO® score? The website myFICO explains:
“A credit score tells lenders about your creditworthiness (how likely you are to pay back a loan based on your credit history). It is calculated using the information in your credit reports. FICO® Scores are the standard for credit scores—used by 90% of top lenders.”
During the housing boom, many mortgages were written for borrowers with a FICO score under 620. While there are still some loan programs that allow for a 620 score, today’s lending standards are much tighter. Lending institutions overall are much more attentive about measuring risk when approving loans. According to the latest Household Debt and Credit Report from the New York Federal Reserve, the median credit score on all mortgage loans originated in the first quarter of 2022 was 776.
The graph below shows the billions of dollars in mortgage money given annually to borrowers with a credit score under 620.
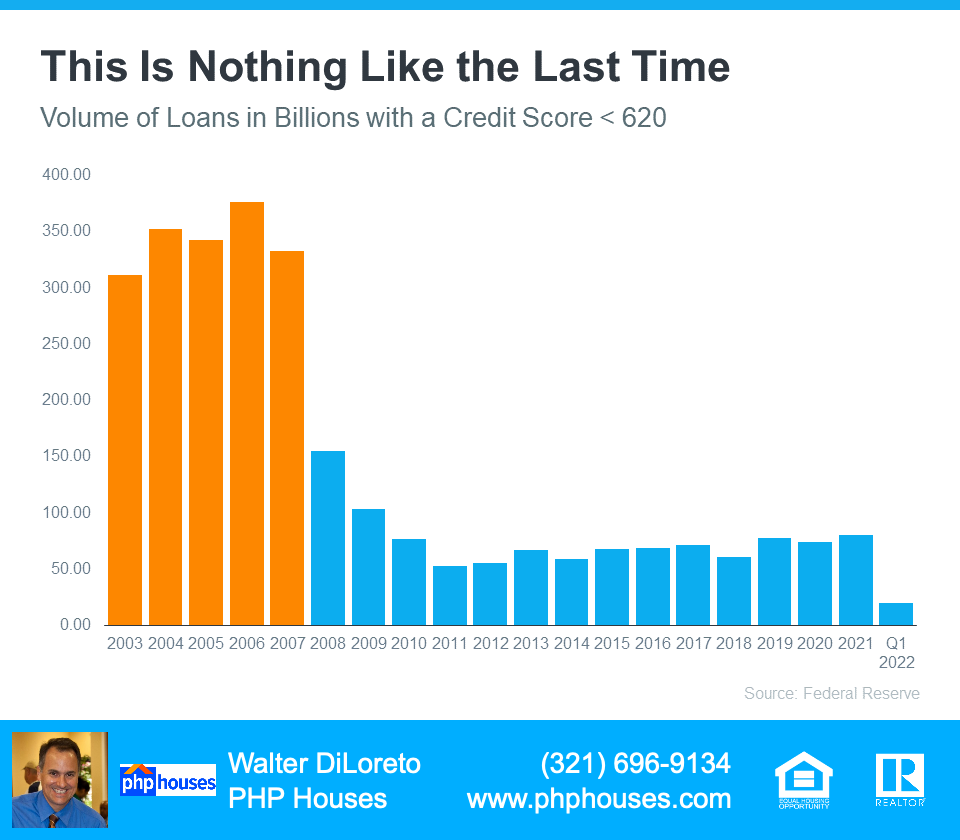
Volume of Loans in Billions with a Credit Score <620
In 2006, buyers with a score under 620 received $376 billion dollars in loans. In 2021, that number was only $80 billion, and it’s only $20 billion in the first quarter of 2022.
Bottom Line
In 2006, lending standards were much more relaxed with little evaluation done to measure a borrower’s potential to repay their loan. Today, standards are tighter, and the risk is reduced for both lenders and borrowers. These are two very different housing markets, and today is nothing like the last time.
Contact us:
PHP Houses
142 W Lakeview Ave
Unit 1030
Lake Mary, FL 32746
Ph: (407) 519-0719
Fax: (407) 205-1951
email: info@phphouses.com
Let’s Connect:
Facebook
Linkedin
Twitter
Instagram
The information contained, and the opinions expressed, in this article are not intended to be construed as investment advice. The author does not guarantee or warrant the accuracy or completeness of the information or opinions contained herein. Nothing herein should be construed as investment advice. You should always conduct your own research and due diligence and obtain professional advice before making any investment decision. The author will not be liable for any loss or damage caused by your reliance on the information or opinions contained herein.